Hong Kong is famous for its vibrant, dynamic and fast-paced business culture. But within this hustle and bustle, companies and employers are subject to a multitude of regulatory responsibilities, including tax obligations.
Among these, one particularly crucial requirement is the annual filing of the Employer’s Return. Understanding this process is not only essential for compliance but also for ensuring that your business operates smoothly within the boundaries of the law.
Here, we’ll delve into the specifics of the forms you need to be aware of, associated filing deadlines, and the critical aspects of record-keeping, to help you navigate through HK tax filing.
Employer’s Return in Hong Kong
As noted above, the Employer’s Return is fundamental to Hong Kong’s tax system. It serves as the official document through which employers report the income and tax deductions of their employees to the Inland Revenue Department (IRD). This annual declaration is necessary to maintain compliance with Hong Kong’s tax laws.
Within the Employer’s Return, there are two key forms: BIR56A and IR56B, each designed to address specific aspects of income reporting.
- Form BIR56A: This form is for reporting the income earned by employees. It includes details on salary, wages, bonuses, commissions, and other taxable income. Employers must complete one BIR56A form for each employee.
- Form IR56B: Form IR56B outlines the list of employees and their respective income details. Employers must complete an IR56B form to provide the IRD with a comprehensive summary of their employees’ income.
Legal Requirements
Completing and submitting the Employer’s Return, including forms BIR56A and IR56B, is more than just good record keeping—it’s the law in Hong Kong. The IRD mandates this annual process, ensuring that employers are transparent in reporting their employees’ income.
Employers are required to furnish this information within one month of the end of the financial year, generally due on or before May 31st of each year. Failing to meet this deadline or providing inaccurate information can lead to penalties or legal actions by the IRD.
Form BIR56A: Employer’s Return of Remuneration and Pensions
Purpose
Form BIR56A serves the purpose of detailing the remuneration and pensions paid to employees during the tax year. It enables the IRD to assess the income tax liabilities of employees accurately.
Who is required to use Form BIR56A?
This form is to be used by all employers in Hong Kong who are paying remuneration and pensions to their employees. It applies to a wide range of employment types, including full-time and part-time workers. Employers must complete a separate BIR56A form for each employee, providing specific details about their income.
Step-by-Step Guide to Completing Form BIR56A
- Employer Information: Start by filling in your business information, including your employer’s tax file number and contact details.
- Employee Details: For each employee, provide their name, Hong Kong Identity Card (HKID) number, and employment income details, including salaries, wages, bonuses, commissions, and any other taxable income. It’s essential to ensure the information is accurate and matches your employee’s records.
- Miscellaneous Income: In this section, detail any miscellaneous income, such as pensions, retirement benefits, or other income received by your employees.
- Total Remuneration and Pensions: Sum up the total remuneration and pensions for each employee.
- Declaration: Once the form is complete, the authorized signatory of your organization should sign and date the declaration.
Form IR56B: Employer’s Return—Employee’s Particulars
Purpose
Form IR56B focuses on providing detailed particulars of each employee. This form is used to report specific information about each employee, such as their employment income, tax payable, and other relevant details.
Who is required to use Form IR56B?
All employers in Hong Kong who pay employment income to their employees are required to use Form IR56B. This form is not limited to full-time employees and also covers part-time and temporary workers. Essentially, any individual who receives employment income in Hong Kong must have their particulars reported on Form IR56B.
Step-by-Step Guide to Completing Form IR56B
- Employee Particulars: Start by providing detailed particulars of each employee, including their name, Hong Kong Identity Card (HKID) number, and employment income details. Ensure that the information is accurate and matches your employee’s records.
- Income Breakdown: Report the employee’s total income, including salaries, wages, bonuses, commissions, and any other taxable income. Additionally, specify any non-employment income or benefits.
- Deductions: Specify any allowable deductions, exemptions, or allowances applicable to the employee’s income, such as child allowances or home loan interest deductions.
- Tax Calculation: Calculate the amount of tax payable by the employee, based on the reported income and deductions. Ensure that the tax calculations are accurate and up-to-date with Hong Kong tax laws.
- Declaration: Once the form is complete, the authorized signatory of your organization should sign and date the declaration, confirming the accuracy of the information provided.
Filing Deadlines and Payment
Important Filing Dates
Like elsewhere in the world, getting your tax filings in before the deadline is extremely important. Especially for the Employer’s Return in Hong Kong, IRD is stringent about deadlines, and missing them can result in penalties. Here are key dates to keep in mind:
Form BIR56A (Employer’s Return of Remuneration and Pensions): This form should be submitted to the IRD within one month of the date of issuance, which is typically in April. The specific date may vary, so it’s essential to check the form for the exact deadline.
Form IR56B (Employer’s Return—Employee’s Particulars): Similar to Form BIR56A, this form should be submitted to the IRD within one month of the date of issuance, usually in April. Again, be sure to check the specific deadline on the form.
Penalties for Late Filing or Non-Compliance
Hong Kong has strict penalties for late filing or non-compliance with tax regulations. Employers who fail to submit their Employer’s Return by the stipulated deadline may face financial penalties. These penalties can vary based on the delay, the number of employees, and other factors. Penalties include:
- A compound penalty of up to HK$10,000 under section 80(1) of the Inland Revenue Ordinance (IRO).
- An estimated tax assessment by the IRD based on the best judgment of the Commissioner.
- A penalty in the form of additional tax under section 82A of the IRO, which may range from 10% to 300% of the tax undercharged or would have been undercharged.
- A court order to comply with the filing requirements within a specified time.
- A prosecution under section 80(2) of the IRO for making false statements or omitting any particulars in the Employer’s Return, which may result in a fine of HK$10,000 and imprisonment for six months.
To avoid penalties, it’s crucial to meet the filing deadlines promptly and accurately.
Making Payments and Calculating Taxes
Accurate calculation and timely payment of taxes are fundamental to the Employer’s Return process. Taxes should be calculated based on the employees’ income, allowances, and deductions. Hong Kong follows a progressive tax system, with tax rates that vary according to income levels. You can refer to the Inland Revenue Department’s tax tables and guidelines to ensure the correct calculation of taxes.
Learn more: Your Guide to Managing Payroll Hong Kong
Options for Electronic Submission and Payment
To streamline the filing and payment process, the IRD encourages electronic submission and payment. E-filing and electronic funds transfer offer convenience and efficiency. Employers can use the “eTAX” online platform provided by the IRD for these purposes. Electronic methods not only reduce paperwork but also allow for quicker processing and acknowledgment.
Record Keeping and Documentation
Importance of Maintaining Accurate Records
It’s the legal responsibility of employers to keep comprehensive records of their employees’ remuneration and related financial transactions. These records serve the following purposes:
- Tax Compliance: Accurate records help ensure that your tax calculations are correct and compliant with Hong Kong’s tax regulations. This is essential for avoiding penalties and other legal issues.
- Employee Relations: Detailed records can help you resolve any disputes or questions that may arise between your organization and your employees regarding remuneration, allowances, or deductions.
- Audits and Inspections: The IRD may conduct audits or inspections of your records to verify your tax compliance. Having organized, complete, and accurate records can make these processes smoother and less time-consuming.
Types of Documents and Records to Keep for Tax Purposes
When it comes to the types of documents and records to maintain for tax purposes, it’s essential to be thorough. Here’s a list of some key documents and records to consider:
- Employment Contracts: Copies of employment contracts for each employee are important for determining salary, benefits, and other conditions of employment.
- Payroll Records: Detailed payroll records should include information on each employee’s income, allowances, deductions, and any other financial transactions related to their employment.
- Tax Records: Copies of tax returns, filing records, and correspondence with the IRD.
- Bank Statements: Bank statements related to your organization’s financial transactions, especially payroll-related transactions.
- Receipts and Invoices: Receipts, invoices, and proof of payment for expenses related to employees’ remuneration, such as allowances and benefits.
Read next: Understanding The Payroll System Hong Kong Runs On
Record Retention Requirements in Hong Kong
Hong Kong’s tax authorities have specific requirements regarding the retention of records. Employers should keep records and documents for at least 7 years. This 7-year period begins on the day you make the records or documents, or when the relevant transaction is completed, whichever is later. These records should be stored in a format that is easily accessible for inspection if required by the IRD.
Optimize Your Employer’s Return Filing with Omni
Managing an Employer’s Return in Hong Kong requires meticulous attention to legal requirements and thorough documentation—especially when the consequences for misfiling can cause significant trouble for your organization. You should strive to minimize human error by leveraging automation to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Omni simplifies the requirements for managing an Employer’s Return in Hong Kong. With secure document storage and straightforward data input, you can quickly access and submit essential information required for tax compliance.
And with payroll solutions that support Hong Kong currency and pay schedules, Omni offers an entire suite of solutions to make your payroll system Hong Kong seamless.
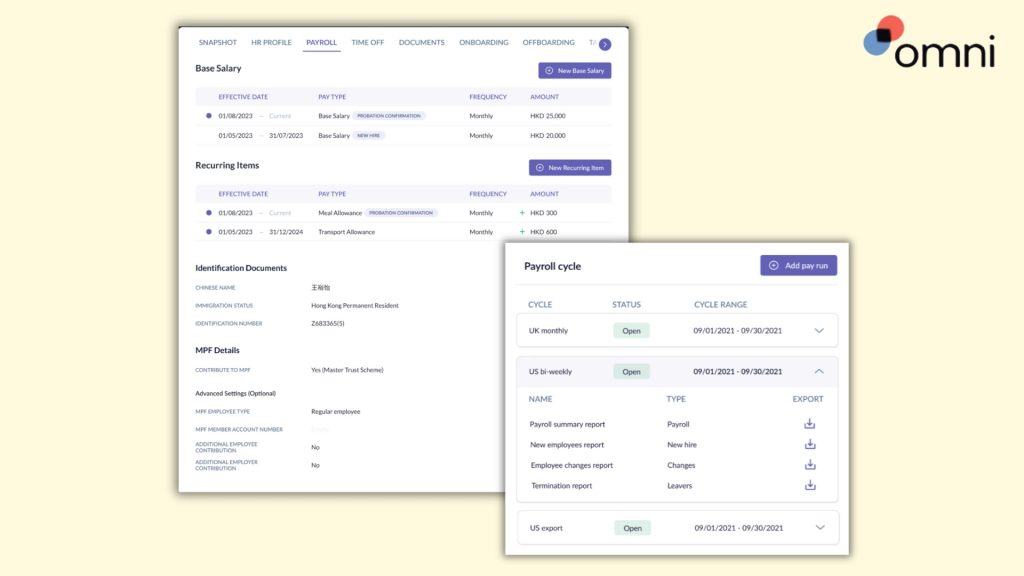
Omni’s comprehensive payroll solution is tailored to Hong Kong’s specific requirements. With features like support for HKD, automated tax calculations, and managed MPF contributions, Omni can help HR teams simplify their payroll processing and tax calculations and ensure compliance with ease, reducing the risk of penalties.
Book a demo with our team to learn more about how Omni can power your HR team with everything from centralized and secure records keeping to accurate and timely payroll processing and tax management.


