According to Deloitte’s survey, 46% of respondents find tax compliance and reporting requirements in Singapore to be straightforward. This percentage is among the highest in the region, trailing only behind Hong Kong, Macau, and Mauritius.
With that in mind, income tax Singapore filing doesn’t need to be stressful, and the different Singaporean taxes doesn’t have to be overwhelming. All you need is a reliable guide on taxation in Singapore to get you started. By doing so, you can ensure your business remains compliant and safeguards its reputation and revenue.
Key Taxes Applicable to Employers
Understanding the SG taxes and Singapore tax rate regulations that the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) sets out, helps keep your business compliant.
Corporate Income Tax
The IRAS collects the Corporate Income Tax Singapore on business profits sourced in the country. The income tax Singapore mandates is a flat rate of 17%. Partial tax exemptions and three-year start-up tax exemptions apply to qualified startups when it comes to this Singapore tax rate.
Goods and Services Tax (GST)
Aside from income tax, Singapore mandates the GST: a consumption tax that you file for the supply of goods and services and the goods imported into Singapore.
If you run a GST-registered business, you have to pay such SG taxes for the selling price of your goods and services at a Singapore tax rate of 9%.
Property Tax
The property tax, another of the required SG taxes, applies to the ownership of immobile properties in Singapore. For your company, a non-residential property, you’re taxed at a flat Singapore tax rate of 10%.
To calculate your property tax, you multiply this Singapore tax rate by the Annual Value (AV) of that property. The AV depends on the value of similar or comparable market rentals.
Payroll Taxes
In Singapore, SG taxes or payroll taxes encompass all tax rates applied to various forms of compensation. While you are responsible for filing your own annual income tax declaration in Singapore, the taxation system does not require you to withhold SG taxes for your employees.
However, despite not having to file taxes like income tax, Singapore’s Employment Act mandates that you withhold certain contributions and levies.
Read more: Payroll Singapore Reference Guide: Everything You Need to Know
Employer’s CPF Contributions
For monthly wages exceeding S$750, employers are required to make contributions to the Central Provident Fund (CPF). This CPF is a government-managed social security fund that supports retirement, housing, and healthcare, funded by contributions from both you and your eligible employees (at a variable Singapore tax rate).
The specific Singapore tax rate deducted from your employee’s salary is determined by their age. Additionally, you are required to make certain CPF contribution rates from your own funds to your employees’ CPF accounts.
Foreign Worker Levy
The system of taxation in Singapore incorporates the Foreign Worker levy as a way to regulate the number of foreign workers in the country.
You pay this monthly income tax Singapore or, more accurately, levy for every employee in your company with a Work Permit or S Pass. The exact Singapore tax rate differs according to your industry, employee qualifications, and the ratio of foreign employees to total employees in your company.
Read next: Singapore Employment Pass: Updates & Requirements in 2023
Skills Development Levy (SDL)
The fund provides support for workforce upgrading programs and offers training grants for when you enroll your employees in training under the National Continuing Education Training. You’re obliged to pay the SDL, which is a Singapore tax rate of 0.25% deducted from your employees’ monthly wages, subject to minimum and maximum contribution limits.
Employer Responsibilities
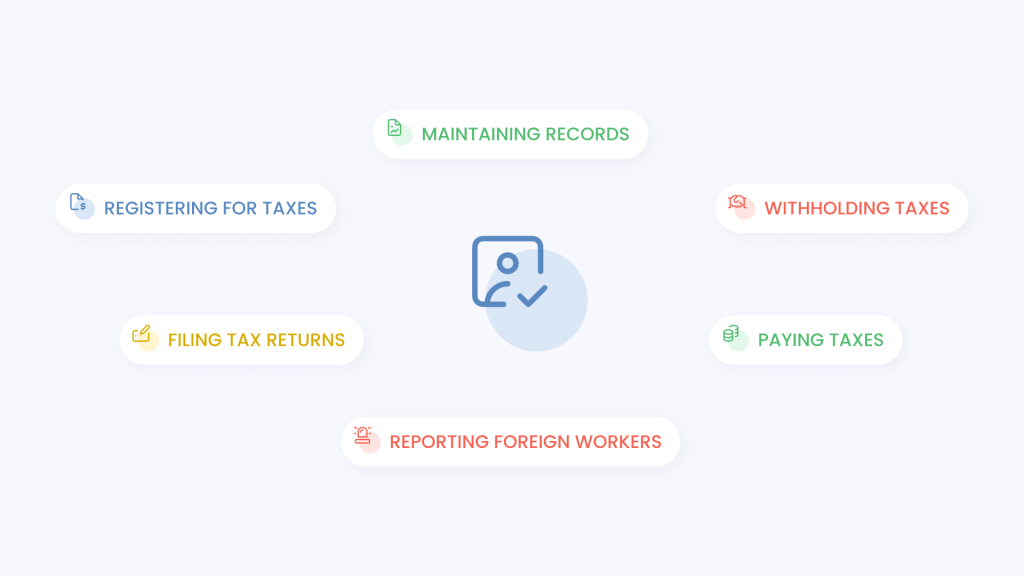
As an employer, it’s important to incorporate these compliance practices for SG taxes into your business operations to ensure adherence to regulations to the Singaporean Employment Act.
Registering for taxes
Before you can pay your income tax, your company needs to be registered for Singaporean taxes. Fortunately, Singapore is ranked as the second easiest country to do business in and the fourth best country to start a business in. To register your business, you’ll need to register with the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) and also register for GST.
Filing tax returns
Tax returns are income tax Singapore forms used to report income, expenses, and other details related to taxes. According to the IRAS, “employers are required by law (S68(2) of the Income Tax Act) to prepare Form IR8A and Appendix 8A, Appendix 8B or Form IR8S (where applicable) for employees who are employed in Singapore by 1 Mar each year.”
The system of taxation in Singapore requires businesses to file tax returns by 15 April each year, with the possibility of later deadlines in some cases. E-filing using the IRS Free File and tax preparation software are available options for filing your taxes.
Paying taxes
This guide to taxation in Singapore aims to assist you in meeting all income tax requirements promptly and accurately. To do so, you must calculate the Singapore tax rate and accurately process and report all payroll components, including benefits, wages, and deductions.
If managing SG taxes seems overwhelming, don’t worry. Payroll software can automate the process, ensuring precise payroll calculations for you.
Maintaining record
Record keeping is crucial when it comes to income tax Singapore. The IRAS says that you should keep records for five years so that you can easily determine the claimed income and business expenses.
Records relate to income or sales and claims or expenses. To authenticate these records, keep receipts, invoices, payslips, vouchers, and other relevant documents to SG taxes. Aside from information about income tax, the regulation requires you to keep records about employees, including the following information:
- Employee Address
- Gender
- Employee NRIC or Work Pass number and date of expiry
- Date of joining of employment
- Employment date of leaving
- Working hours (including breaks duration)
- public holidays and leaves used
Withholding taxes
A unique aspect of taxation in Singapore is that you are not required to withhold SG taxes from your employees’ monthly salaries. However, you must withhold certain Singapore tax rate variations, such as contributions and levies.
Reporting foreign workers
According to the IRAS, you must submit employment income information for foreign workers in Singapore for the respective year.
Employers are required to use the Foreign Identification Number (FIN) issued to foreign employees by the Ministry of Manpower (MOM) or Immigration and Checkpoints Authority (ICA) in their AIS submissions. This reporting enables you to pay the relevant Singapore tax rate, known as the Foreign Worker levy.
Struggling to understand the Singaporean Employment Act?
Key Steps for Preparing Employee Income Tax
If you’re still uncertain about taxation in Singapore, let’s get straight to the point and provide you with the steps for preparing employee income tax, Singapore edition.
1. Understanding your responsibilities as an employer
Understanding your responsibilities as an employer makes Taxation in Singapore straightforward. You must file employee earnings, submit specific tax forms, and ensure accurate application of the correct Singapore tax rates.
2. Determine tax withholding for your employees
Now is the time to calculate the amount you should withhold for SG taxes, including contributions, deductions, and levies on behalf of your employees. Unless the Singapore tax rate is fixed, you’ll need specific data, such as employee age or qualifications, to determine the IRAS rate.
3. Stay updated with tax regulations
Tax regulations get updated regularly, and their complexity and the pace by which they change has increased. Staying up to date with taxation in Singapore enables you to file the correct documents and pay the correct Singapore tax rate.
You can check the IRAS Overview of Tax Changes for the financial year 2024, which includes changes to tax incentive schemes, tax deductions, and the Singapore tax rate.
4. Utilize payroll software
As you may have discovered, payroll software simplifies the management of taxation in Singapore. With payroll software, you can calculate the income tax Singapore regulations require you to pay, subtract deductions, calculate benefits, bonuses, and paid leave, generate payslips, and easily store, access, and manage payroll and employee data.
Additionally, it automates various payroll processes, ensuring accuracy and compliance, and saving you time and money on SG tax management.
5. Prepare for reporting deadlines
Preparing for reporting deadlines for taxation in Singapore requires careful planning and organization.
It is essential to keep accurate records of income, expenses, and other financial transactions throughout the year. Employers should ensure that they have the necessary information and forms ready for reporting deadlines, such as Form IR8A for employee income.
Understanding the specific deadlines set by IRAS is crucial to avoid late filing penalties.
Ensuring Compliance with Singaporean Tax

The primary objective of understanding taxation in Singapore and abiding by SG taxes is to avoid penalties, fines, and legal action. Here are some ways on how you can ensure compliance:
Stay updated with regulations
Staying updated with regulations is crucial for managing taxation in Singapore.
Fortunately, certain payroll providers stay abreast of regulatory changes to income tax Singapore and notify you about every update. What’s more, some all-in-one HR systems offer real-time compliance updates.
Register with IRAS
Taxation in Singapore starts with registering your business. The Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) enables you to register your business online in one to two days. The process looks like this:
- Getting the business name approved
- Preparing the needed documents
- Submitting the application to ACRA
Note that you’ll have to register for the GST Singapore tax rate. This process is composed of the following steps:
- Choosing the GST registration type
- Completing the e-learning course
- Submitting the GST tax application
Maintain accurate records
You’re aware of the need to maintain records of your income/sales, claims/expenses, income tax Singapore forms, and employee information (including source documents and bank statements) for five years. However, managing every Singapore tax rate manually without encountering false, missing, or outdated data can be difficult.
Fortunately, the IRAS provides a checklist for record keeping. Also, payroll software solutions help ensure error-free records by creating digital copies of employee payslips, assisting with timesheet management, and calculating your employees’ time off and attendance.
Identify applicable taxes
Identifying the SG taxes that apply to your business and employees is crucial to ensuring that you pay the correct amount. It is also important to identify any tax breaks, deductions, and grants that apply when calculating each Singapore tax rate. For instance, you must pay the Foreign Worker Levy for your foreign employees.
File returns and pay taxes on time
To manage taxation in Singapore, you must make tax payments and file returns on time, which is one month after you receive the Notice of Assessment (Tax Bill). If you don’t make the deadline the income tax Singapore requires, you may be subjected to a 5% penalty and enforcement action, such as a travel restriction order or legal action.
Train your employees
It is crucial to train your employees to ensure compliance with SG tax regulations. Proper training can help them understand their roles and responsibilities regarding tax reporting and payment, reducing the risk of errors or non-compliance.
Additionally, training can help employees stay updated with changes in Singapore tax laws and regulations, ensuring that your business remains compliant. By investing in training, you can help your employees perform their tax-related duties accurately and efficiently, ultimately avoiding penalties and legal issues.
Conduct regular reviews
Tax reviews are routine assessments that encompass all facets of taxation in Singapore. They enable you to verify compliance with obligations, identify opportunities for tax savings, reduce the tax burden, and manage risks effectively.
Utilize payroll software
Streamline the process of taxation in Singapore with payroll software services. These services automate numerous payroll processes such as calculating SG taxes, deductions, bonuses, benefits, and hours worked, issuing payslips, generating the necessary forms for income tax Singapore demands, and storing data securely.
This approach helps reduce errors, ensures data security, promotes compliance with tax regulations, and facilitates effective filing of SG taxes.
Automating Singapore Tax Compliance with Omni
Managing taxation in Singapore is a complex and detail-oriented task that demands a deep understanding of the region’s unique legal requirements and a commitment to accuracy and compliance. That’s why it’s important to have the right technology on your side.
Omni offers a comprehensive payroll solution tailored to Singapore’s specific requirements. With features like support for SGD, automated tax calculations, and managed CPF contributions, Omni can help HR teams simplify their payroll processing and ensure compliance with ease.
Omni’s suite of features makes the requirements for running a compliant and efficient payroll system in Singapore easy. With secure and centralized employee records, HR teams can swiftly access employment contracts and essential documents that support payroll practices.
Our time and attendance features empower teams to automate data and produce accurate reports in minutes, making payroll calculations seamless and accurate. And with payroll solutions that support SGD and pay schedules, Omni offers an entire suite of solutions to make your payroll system Singapore seamless.
If you’re ready to take your payroll Singapore management to the next level, book a demo with us today. We’ll walk you through the platform’s capabilities and demonstrate how Omni can transform your payroll processing, saving you time, reducing administrative burdens, and enhancing overall efficiency.


