In the heart of Southeast Asia, Singapore thrives as a hub of innovation and economic prowess. For many professionals, this vibrant city-state represents a realm of unparalleled career opportunities and a high quality of life.
But before foreign workers can jump into their Singapore career, there’s one step that needs to be taken first—the Employment Pass (E Pass).
This critical document not only offers a working visa but serves as a conduit for personal and professional growth. And recently, the regulations around accessing the E Pass and the E Pass salary requirements have evolved, and the COMPASS framework is part of it.
Here, we’ll dive into the core elements of Singapore’s E Pass and E Pass Salary information, and take a look at recent updates, including the introduction of the points-based Complementarity Assessment Framework (COMPASS framework) and revised minimum salary requirements.
2024 Updates and Requirements

As Singapore continues to evolve as a global business hub, it continually refines its policies and requirements regarding foreign work passes to maintain its competitive edge while safeguarding opportunities for local talent.
Staying informed about these changes and the COMPASS framework is crucial for employers, HR professionals, and aspiring expatriates alike.
New Minimum E Pass Salary Requirements
The qualifying E Pass salary is SGD 5,600 for most sectors, except financial services. For those in financial services, the minimum E Pass salary stands at SGD 6,200. This salary requirement progressively increases with age, reaching up to SGD 10,700 (for most sectors) and SGD 11,800 (for financial services) for individuals aged 45 and above.
As for existing EP holders, EPs expiring from 1 January 2026 will need to meet the revised qualifying salary. This new E Pass salary framework emphasizes both the value of experience and skill set, ensuring that foreign talents align with Singapore’s evolving workforce needs.
Learn more: Payroll Singapore Reference Guide
The COMPASS Assessment Framework
Effective from 1 September 2024, new E Pass salary candidates will encounter a new requirement, the Complementarity Assessment Framework (COMPASS framework). Alongside meeting the E Pass salary qualifications, candidates will need to navigate the COMPASS framework evaluation to determine their eligibility.
The second stage involves the COMPASS framework scoring system, which applies to all candidates unless exempted. To secure an E Pass, candidates need to amass a minimum of 40 points across various criteria within the COMPASS framework. These include:
- E Pass Salary: The COMPASS framework evaluates the candidate’s fixed monthly salary according to sector-specific benchmarks, assigning points based on how well the salary aligns with local standards.
- Qualifications: The COMPASS framework mandates that candidates’ qualifications are authentic and awarded by accredited institutions, requiring verification proof for post-secondary diploma and above qualifications from background screening companies and government/awarding institution portals. Under the COMPASS framework, you want to target applicants from top-tier institutions or, at least, degree-equivalent qualifications.
- Diversity (Firm-Related): The COMPASS framework encourages employers to diversify their foreign professional workforce by awarding points for hiring candidates from underrepresented countries or regions.
- Support for Local Employment (Firm-Related): Under the COMPASS framework, employers are prompted to display efforts in supporting local employment. Points can be earned by surpassing expectations in areas like job advertising and fair consideration.
In addition to the fundamental criteria, the COMPASS framework factors in bonus points based on the candidate’s specialized skills and alignment with Singapore’s strategic economic priorities and potential contribution to Singapore.
The introduction of the COMPASS framework ensures greater transparency, quality, and diversity in E Pass salary applications. Employers can benefit from the enhanced Self-Assessment Tool (SAT) to confirm candidate eligibility before applying.
Since 1 March 2024, successful candidates are no longer required to get COVID-19 vaccination for E Pass issuance or for the COMPASS framework; however, it’s a preferable protection measure.
The COMPASS framework exempts some applicants. If you’re paying your future employee a fixed monthly salary of at least SGD 22,500, are applying for an intra-corporate transferee, or are applying for someone to work for up to a month, they don’t need to meet the conditions set by the COMPASS framework.
Immigration Policies
One notable update in Singapore’s immigration policies came into effect on 11 March 2022.
The Ministry of Manpower (MOM) introduced an innovative approach by replacing traditional inked endorsement stamps on passports with electronic Visit Passes (E Passes). This not only streamlines the immigration process but also underscores Singapore’s commitment to harnessing digital solutions in managing immigration.
Updates on the Dependent Pass and S Pass Quota
Since 1 May 2021, Dependent Pass (DP) holders seeking employment in Singapore have encountered a transformative change. DP holders now need to qualify for and obtain their work passes, such as E Passes, S Passes, or Work Permits, to work in Singapore.
As a result, the concept of dependency on the main pass holder has been redefined, granting DP holders increased autonomy in their work and stay privileges. Their DP will need to be canceled before their E Passes or S Pass is issued, signifying a significant shift in the dynamics of employment for DP holders.
Another update is the gradual increase in the minimum qualifying salary for S Passes. Starting from 1 September 2023, the minimum salary for S Pass holders will increase in three stages. The first increase took effect for both renewals and new applications, followed by a second increase for renewals in 2024. The final increase will apply to both new applications and renewals in 2025 and 2026, respectively.
The exact salary amounts will be determined based on local average wages at the time of each increase, but the minimum will be at least SGD 3,150 for all sectors and SGD 3,650 for financial sectors.
Understanding the Singapore Employment Pass
In Singapore, the E Pass is an essential work visa that allows foreign professionals, managers, executives, and skilled workers to live and work in the city-state (after passing the point-based COMPASS framework).
It is a vital document for expatriates, opening doors to numerous career opportunities and experiences in Singapore.
To give you a comprehensive understanding of the Singapore Employment Pass and the E pass salary regulations, let’s break down their key aspects:
Eligibility Criteria
The E Pass is designed for individuals who meet specific requirements, including minimum salary levels, educational qualifications, and relevant work experience. The eligibility criteria are meticulously designed to ensure that foreign professionals and workers add value to Singapore’s workforce.
Types of Employment Passes (EP) Available
The Singaporean government has introduced different categories of Employment Passes to cater to varying skill levels and industries. The 3 primary types include:
Employment Pass for Professionals
The Employment Pass for Professionals is the most common type. It’s typically designed for mid to high-skilled professionals who hold recognized qualifications. Applicants should have an offer of employment in a managerial, executive, or specialized job role. The minimum monthly E Pass salary required varies based on factors like the applicant’s age and the sector of employment, but it typically starts lower for young professionals and goes up as they gain experience.
S Pass for Mid-Skilled Workers
The S Pass is intended for mid-skilled workers, offering a more accessible option for those who may not qualify for the Employment Pass. Eligibility is based on the applicant’s qualifications, experience, and the employer’s compliance with quotas on S Pass holders.
Miscellaneous Work Pass for Short-Term Work
The Miscellaneous Work Pass is designed for individuals who need to perform short-term, non-conventional work in Singapore. It is generally used for activities that don’t fall under standard employment categories.
These categories cater to a wide spectrum of workers, from highly skilled professionals to those in mid-skilled positions and even individuals engaged in short-term projects. Understanding these categories is crucial when applying for the right Employment Pass and ensuring compliance with Singapore’s immigration laws. In the subsequent sections, we’ll delve into E Pass salary requirements and other critical details for each category.
Application Process
Applying for an E Pass in Singapore is a meticulous process, designed to ensure a smooth entry for foreign professionals into the country.
Step-by-step guide to applying for an Employment Pass
Step 1: Submit an application. Your journey begins with the submission of an online application for the E Pass. Employers (or their appointed employment agents) can start this process.
Ensure the candidate meets the necessary qualifications by using the Self-Assessment Tool (SAT) and calculating your score in the COMPASS framework. The processing time for this initial application stage typically takes place within 10 business days.
Step 2: Receive the In-Principle Approval (IPA). Once your application successfully passes the initial stage, you will receive an In-Principle Approval (IPA) letter. This letter is a significant milestone, serving as a pre-approved single-entry visa for the candidate to enter Singapore. The IPA also specifies whether the candidate needs to undergo a medical examination.
Step 3: Request MOM to issue the E Pass. With the IPA in hand, employers should proceed to request the Ministry of Manpower to issue the Employment Pass.
Step 4: Receive the notification letter. Employers will receive a notification letter, marking another pivotal point in the process. If deemed necessary, you can extend the validity of this letter should candidates require additional time for card registration procedures.
Step 5: Register fingerprints and have photos taken. Candidates will need to register their fingerprints and have their photo taken at MOM if indicated. This step is usually immediate.
Step 6: Receive the Employment Pass card. The culmination of this process is the issuance of the actual Employment Pass card. Authorized recipients or candidates themselves will receive this card within 5 working days after fingerprint and photo registration or document verification.
Required Documents and How to Prepare Them
Before embarking on the E Pass application journey, it’s essential to ensure you have the necessary documents ready:
- Proof of qualifications, which should be authentic and awarded by accredited institutions.
- Written consent from the candidate to apply for the E Pass on their behalf.
- Verification proof for post-secondary diploma and above qualifications.
Online Application Process
Employers can easily apply for the E Pass through the E Pass online portal on the Ministry of Manpower’s website. The process involves the submission of required documents and payment of processing fees.
Processing Times and Fees
Processing time for E Pass applications typically occurs within 10 business days. However, For overseas companies without a Singapore-registered office, the processing time may take up to 8 weeks.
The application fee for an E Pass is SGD 105, and the issuance fee is SGD 225. But there are several other fees you might incur, based on factors such as the type of the employing company and the desired duration of the pass.
These fees are meant to contribute to the resources required to ensure a streamlined application process for E Passes in Singapore.
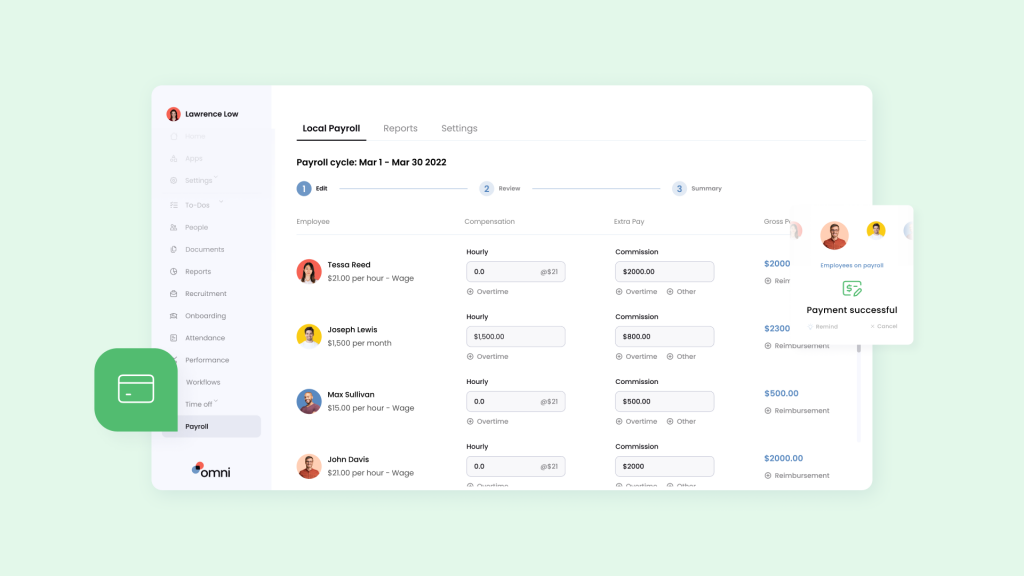
Securely Navigate Employee Data and E Pass Salary Management With Automation
In Singapore, the E Pass is far more than just a visa—it’s a ticket to one of the most dynamic and economically vibrant destinations in the world. This vital travel document enables both professionals and businesses to become part of Singapore’s thriving business community, contributing to its growth while reaping the benefits of a world-class living environment. By ensuring that they receive at least the minimum e pass salary, MOM regulates that economic growth.
In the backdrop of these E Pass salary, COMPASS framework, and other regulatory changes, technology can help manage the various documents and E Pass salary requirements needed to support your foreign talent.
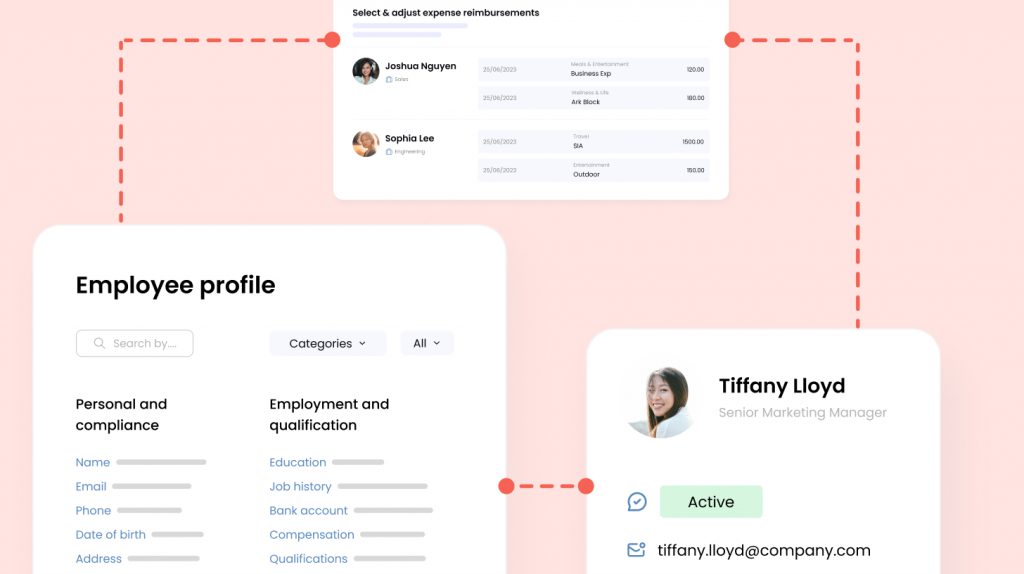
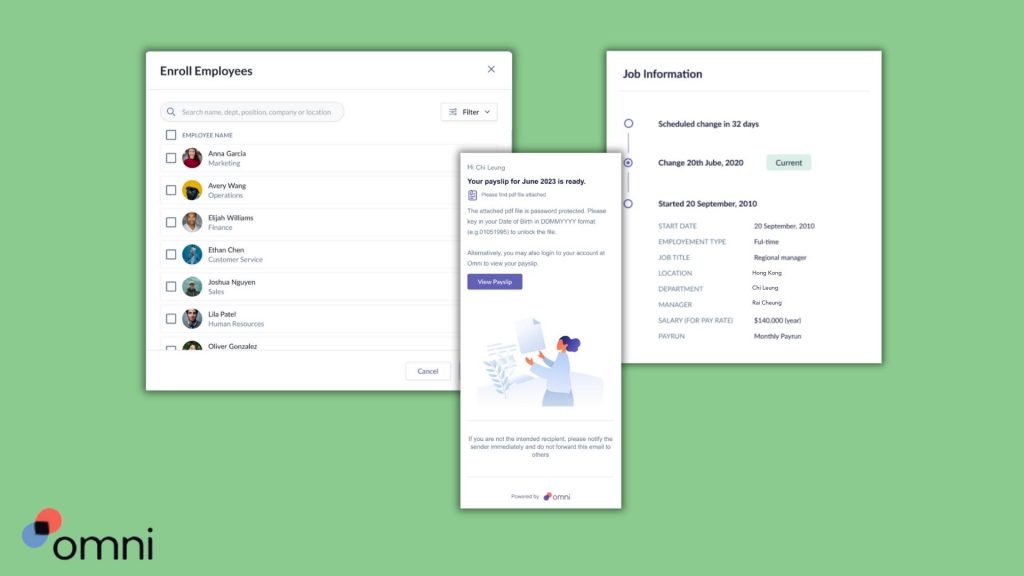
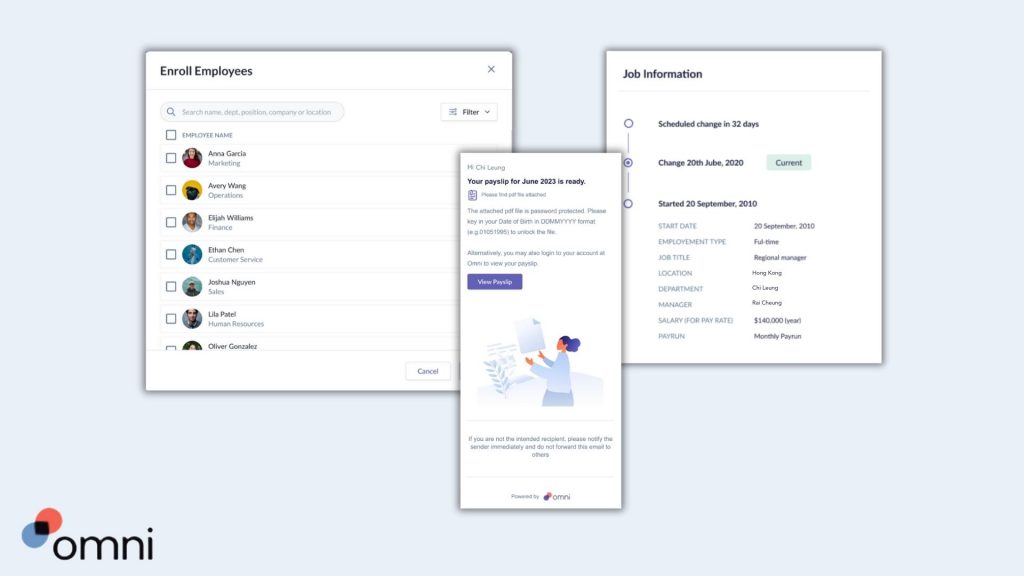
Omni allows your organization to securely and centrally manage employee information, such as proof of qualifications and written consent necessary to obtain a Singapore E Pass.
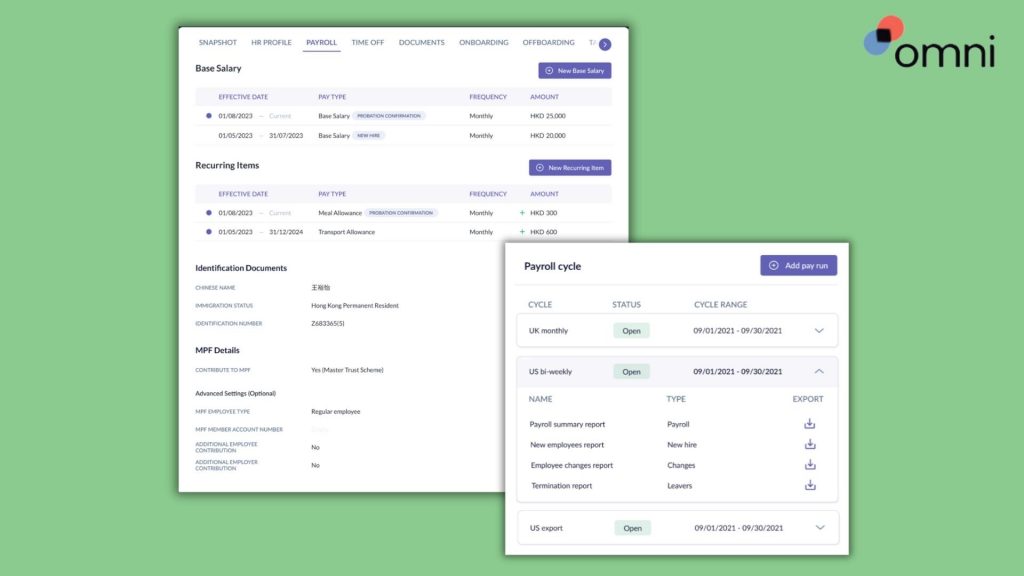
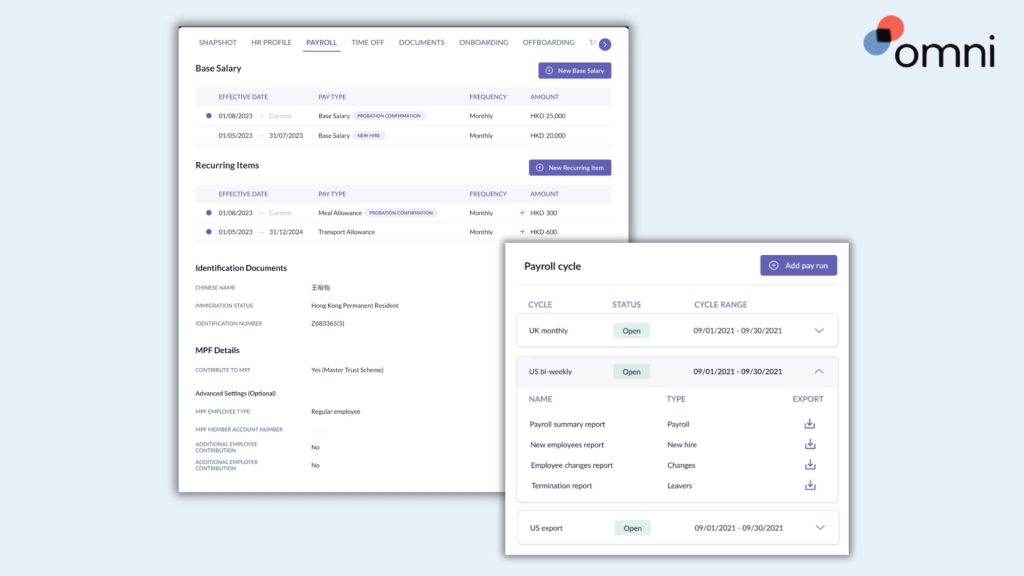
Our employee-portal makes it easy for employee’s to upload and update their information, centralizing critical information, including E Pass salary minimums, expiry dates, and renewal reminders. This ensures your E Pass management meets the regulations set by the Singapore government.
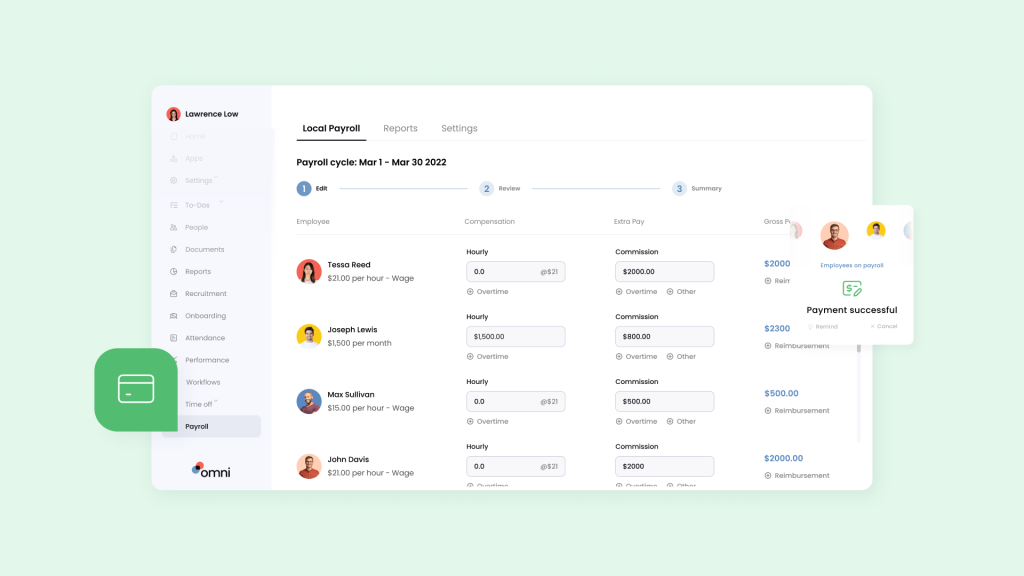
With localized payroll, Omni can help your team process each E Pass salary with ease. Omni offers a comprehensive payroll solution tailored to Singapore’s specific requirements about E pass salary ranges, benefits, and overtime.
With features like support for SGD, automated tax calculations, and managed CPF contributions, Omni can help HR teams simplify their payroll processing and ensure compliance.
With our automated payroll software Singapore, digitized and secure pay slip distribution, and dedicated support teams to guide your team and ensure compliance, Omni’s payroll processing reduces the administrative burden of your HR team and frees up valuable time to dedicate to more impactful business processes.
And with the COMPASS framework, you’ll see the effectiveness of OMNI management and practices, creating the progressive, inclusive environment you dream of. After all, our expert support and assistance is tailored to your businesses unique requirements and local regulations.
Book a demo today, and learn how Omni can help you streamline your E Pass salary payroll processes and expertly navigate Singapore E Pass management to ensure compliance for your organization.