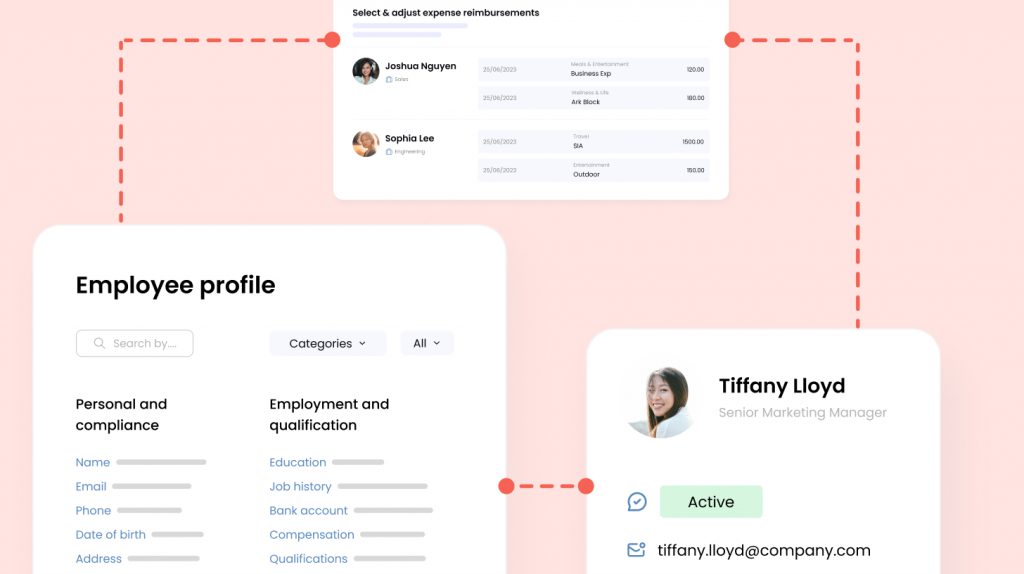
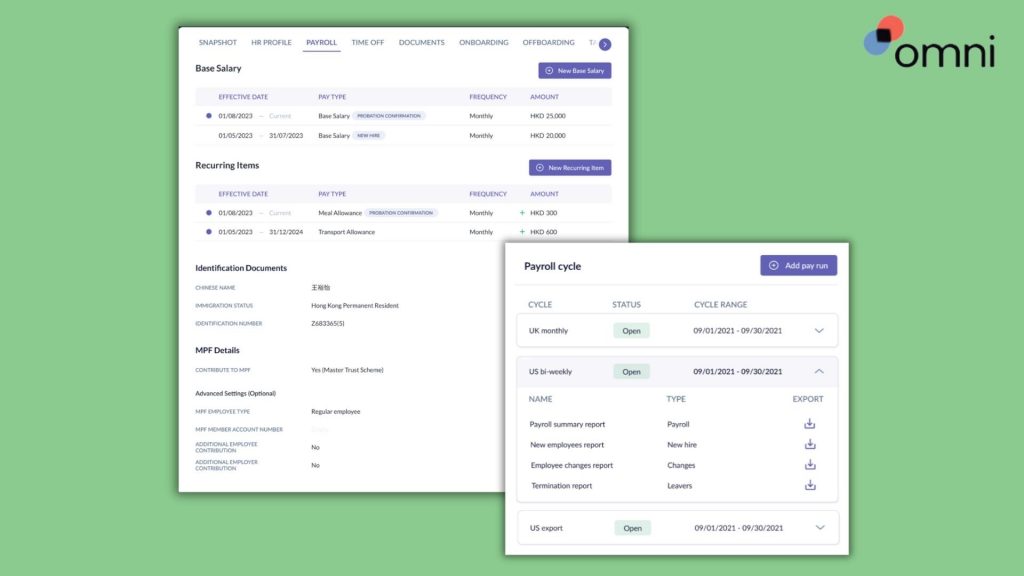
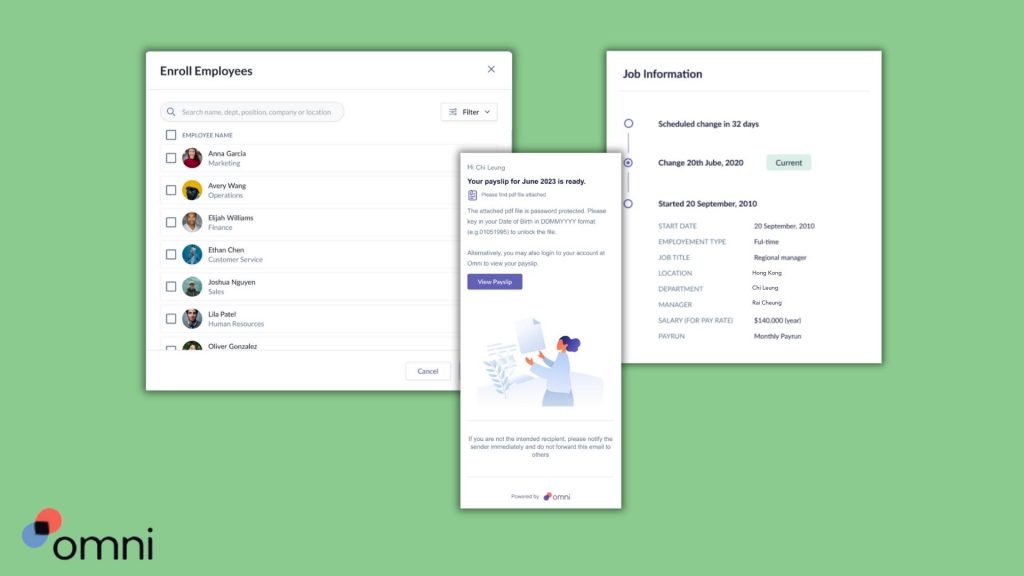
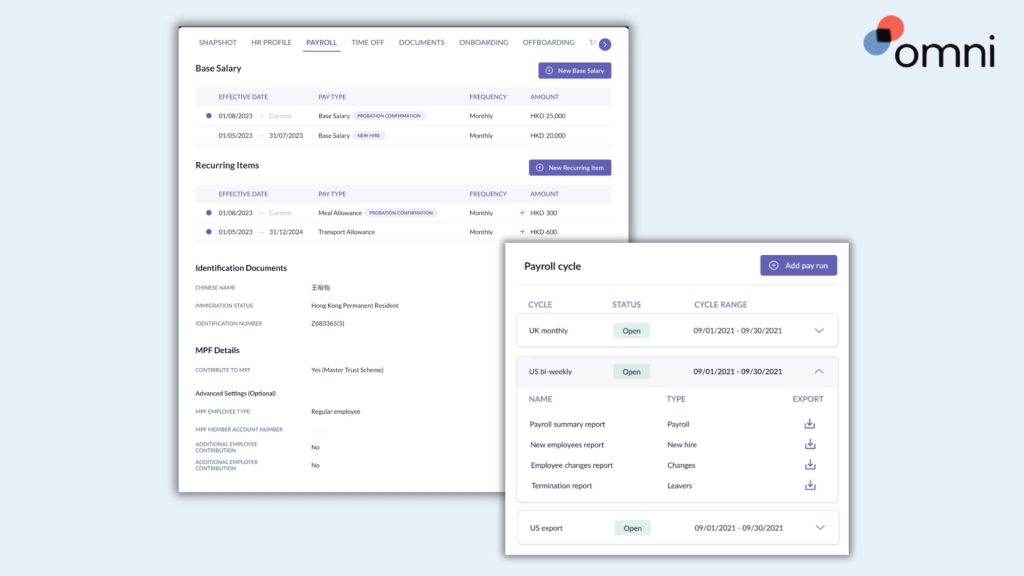
Whether you’re an active business owner, manager, or HR professional, payroll is a crucial part of keeping a business running and your employees engaged. For those in Singapore, payroll comes with a set of complex regulations that require careful adherence to remain compliant with local laws.
With all of the responsibilities on your plate, from managing a comprehensive onboarding program to cultivating a culture of continuous learning within your organization, routine payroll functions like itemized payslips can easily become a nuisance on your to-do list. Which is why many are turning to a payslip template Singapore companies can use to simplify their payroll process.
The payslip template Singapore makes it easy to share key payroll information such as absentee payroll and CPF deductions that make up running payroll in Singapore. Let’s take a look at the government mandated requirements for Singapore payslips to help guide you through utilizing our payslip template Singapore.
Understanding Singapore Payslip Requirements
According to the Ministry of Manpower (MoM), effective 1 April 2016, all employers must issue itemized pay slips to employees covered by Singapore’s Employment Act.
Here are the detailed requirements such as what items to include, when and how to give them.
Requirements
Employers must issue itemized pay slips to all employees covered by the Employment Act.
When
- At the time of payment to the employee.
- If unable to give at the time of payment, to be given within three working days of payment.
- In the case of termination or dismissal, must give pay slip together with outstanding salary.
Format
Soft or hard copy (including handwritten).
Items to include
Pay slips must include, where applicable, the below items.
For example, if your employees are not eligible to receive overtime pay, your pay slip need not include items 9 to 11.
If payments are made more than once a month, employers can consolidate pay slips. The consolidated pay slip must contain details of all payments made since the last pay slip.
- Full name of employer.
- Full name of employee.
- Date of payment (or dates, if the pay slips consolidates multiple payments).
- Basic salary
For hourly, daily or piece-rated workers, indicate all of the following:
Basic rate of pay, e.g. $X per hour.
Total number of hours or days worked or pieces produced. - Start and end date of salary period.
- Allowances paid for salary period, such as:
All fixed allowances, e.g. transport.
All ad-hoc allowances, e.g. one-off uniform allowance. - Any other additional payment for each salary period, such as:
Bonuses
Rest day pay
Public holiday pay - Deductions made for each salary period, such as:
All fixed deductions (e.g. employee’s CPF contribution).
All ad-hoc deductions (e.g. deductions for no-pay leave, absence from work). - Overtime hours worked.
- Overtime pay.
- Start and end date of overtime payment period (if different from item 5 start and end date of salary period).
- Net salary paid in total.
Maintaining records
Employers must keep a record of all payslips issued in soft or hard copy, including handwritten.
- For current employees: Latest two years.
- For ex-employees: Last two years, to be kept for one year after the employee leaves employment.
Why Use an Itemized Payslip Template Singapore?
Creating itemized payslips can be time consuming and prone to error. By utilizing the payslip template Singapore, you save time by eliminating the need to recreate payslips for each employee.
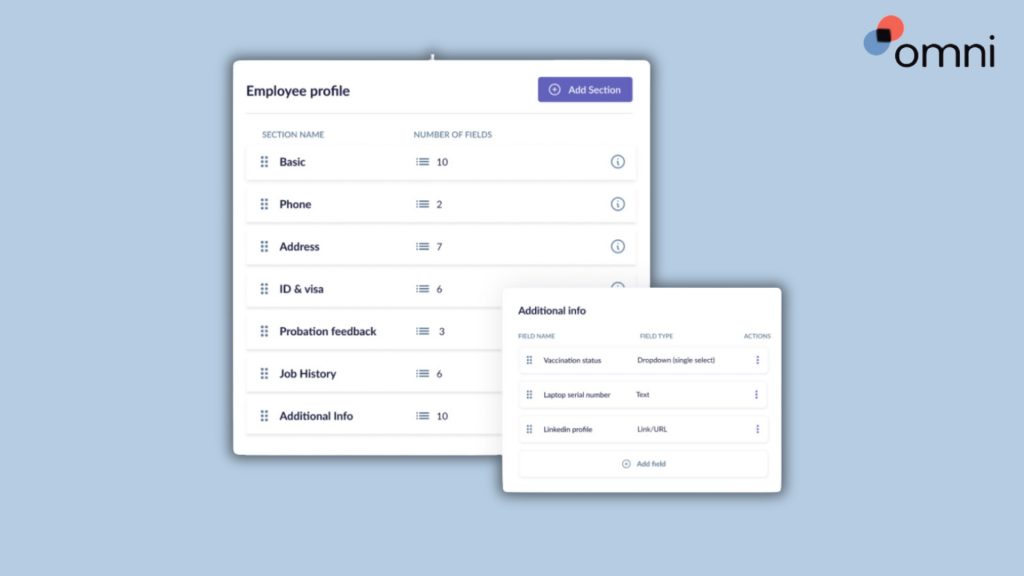
With dedicated prompts, our payslip template Singapore works as a visual checklist helping you ensure you include all necessary information, reducing payroll errors and helping you remain compliant with local regulations.
Whatsmore, the payslip template Singapore provides a uniform and professional layout bringing consistency to your payroll process. By customizing your payslip template Singapore, you can provide your employees with a branded payslip that presents a united employer brand.
Customizing Your Payslip Template Singapore

A little customization can go a long way! Here are some key ways you can make our payslip template Singapore your own.
- Include your brand’s logo
- Change the payslip template Singapore colors to your brand’s colors
- Include additional itemized fields or remove fields that do no apply to your team
Making these small tweaks to your payslip template Singapore help bring your brand’s unique look and feel to your payroll process.
Common Mistakes in Payslip Preparation
Miscalculations
When it comes to payroll, calculations are crucial, but managing many employees with varying pay grades, benefits, and time-off can result in miscalculations. Common mistakes include:
- Taxes: tax rates are known to shift, and companies that fail to keep up with the changing tax rates and tables are at risk for miscalculations, which can result in fines.
- Payroll: particularly common for hourly employees, miscalculations for payroll happen when the number of hours or and rate of pay are incorrectly calculated.
- Overtime: Overtime is often calculated separately from regular rate-of-pay. Depending on your company’s policy, it’s important to take great care in calculating overtime pay as it’s a common error in payroll.
Typos
Let’s face it, everyone makes mistakes. Manually entering information like employee names or bank account numbers for direct deposit can easily result in errors. This can result in delayed payments, inaccurate records, or even deposits being delivered to incorrect accounts.
Missed deadlines
When managing multiple employees and various deadlines—especially if you’re managing a globally distributed team—can easily result in missed deadlines for filing. This can result in fines to your company, and frustrations among your staff.
Misclassification of workers
Mistake in the classification of the workers is one of the most common mistakes in payroll. Companies often have two types of workers including full-time employees and freelancers or contractors working in flexible conditions within the company.
Guidelines for Enhancing Payroll Accuracy and Efficiency
Making sure your employees get paid correctly and on time is a big deal for any business. To avoid mistakes and keep things running smoothly, here are some simple things you can do:
Stay updated on regulations
Stay updated on the local, state, and federal laws about payroll. Make sure you understand stuff like taxes, minimum wage, and overtime. Check government websites or talk to legal experts to be sure you’re following the rules.
Maintain records
Keep track of all the important info for each employee. This includes personal details, tax forms, bank info, salary history, and any work agreements. Double-check this info regularly to catch any mistakes.
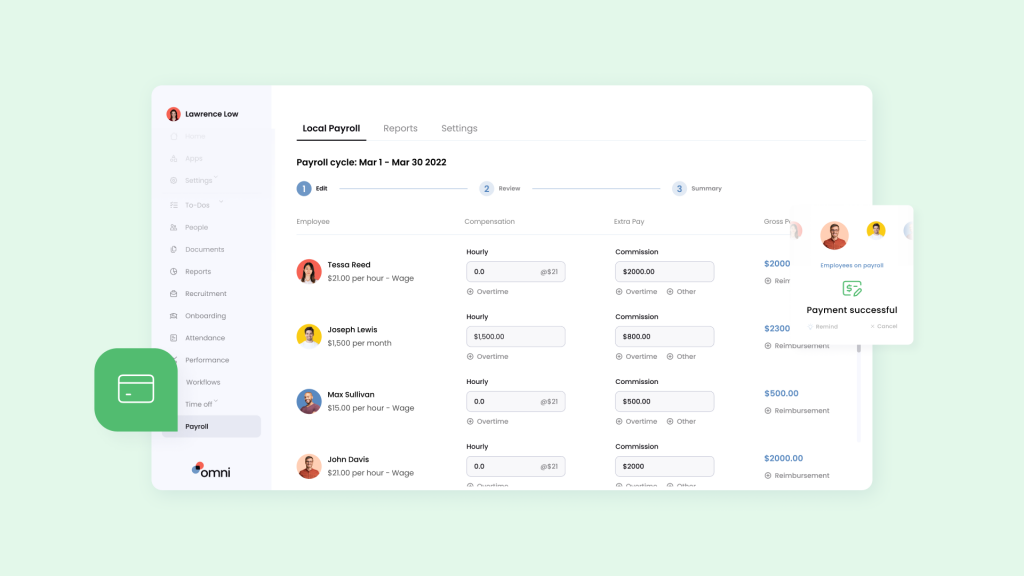
Use a payroll software
Invest in reliable payroll software for Singapore that fits your business needs. A good system can do the math for you, handle taxes, and make pay stubs. Look for software that works well with your accounting system and does things like updating tax info.
Automate, automate, automate
Doing things by hand can lead to mistakes. Use automation for tasks like calculating pay, deducting taxes, and administering direct deposits for faster, more efficient payroll and HR functions.
Check your math
Even if you’re using a computer, it’s smart to double-check the numbers. Review your payroll regularly to make sure everything adds up, like taxes, deductions, overtime, and any special payments.
Use a payroll calendar
Make a schedule for when you do payroll, when taxes are due, and when you need to report stuff. This helps you stay on top of everything and not miss any deadlines.
Train your payroll team
Make sure your team knows how to do payroll and use the software. Keep them in the loop about any changes in the rules or procedures. Give them resources like manuals or online training to help them out.
Keep an eye on your accounts
Check your payroll accounts regularly and compare them with your financial records. This helps you catch any mistakes and keep everything accurate.
Perform regular checks
Look into your payroll processes and records from time to time. Check if you’re classifying employees right, if the hours are recorded correctly, and if the reports match up. Fix any problems you find.
Get help if you need it
Payroll can be tricky, and mistakes can cause big issues. If you’re not sure about something, think about getting help from payroll outsourcing Singapore. They can handle the hard stuff like processing payroll, filing taxes, and making sure you follow the rules.
Streamline Your Payroll Services with Omni

Manual payroll is made easier with tools like our payslip template Singapore, but companies are still at risk of common errors such as miscalculations, typos, and missed deadlines. Not to mention the burden of mandatory records management.
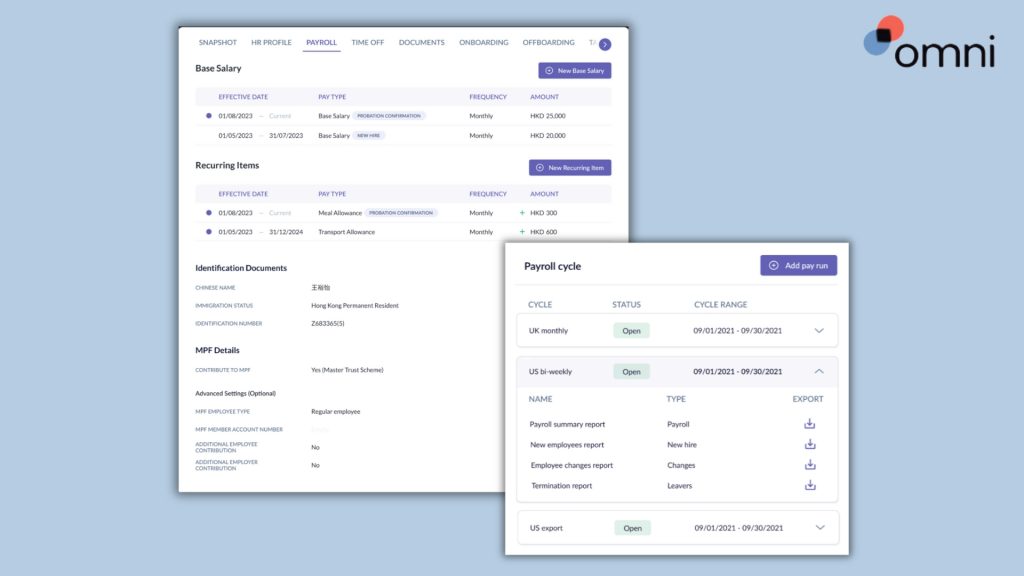
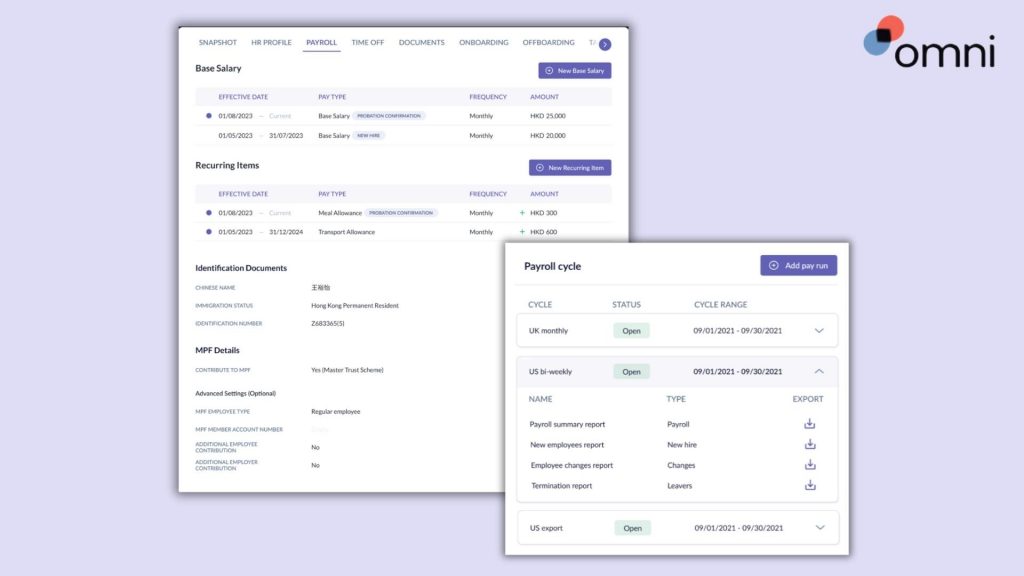
Automating your payroll with Omni offers a comprehensive payroll solution tailored to Singapore’s specific requirements. With features like support for SGD, automated tax calculations, and managed CPF contributions, Omni can help HR teams simplify their payroll processing and ensure compliance with ease.
With automated payroll outsourcing services, digitized and secure payslip distribution and records keeping, and dedicated support teams to guide your team and ensure compliance, Omni’s payroll processing reduces common payroll errors as well as the administrative burden of your HR team and frees up valuable time to dedicate to more impactful business processes.
Our expert support and assistance is tailored to your businesses unique requirements and local regulations. Book a demo today and learn how Omni can help you streamline your payroll processes and minimize the costs associated with common errors.