The development of paid maternity leave under labor law Malaysia aims to provide a more inclusive workplace for women, recognizing the life transition they undergo when welcoming a newborn and the importance of bonding and health recovery. Maternity leave Malaysia remains a protected right.
However, there is a growing advocacy among employees for better work-life balance to improve productivity. The introduction of paternity leave also acknowledges the father’s role in childcare. As organizations are beginning to embrace parental leave Malaysia, it shows that children are the shared responsibility of both parents, rather than a burden in the workplace.
Employers and HR professionals striving to create a supportive company culture must stay updated with new policies to provide the necessary parental support for their employees. Creating a culture that supports parental leave Malaysia is beneficial for both employers and employees.
Do employees get parental leave Malaysia?
The amendments made to the Employment Act have given both fathers and mothers the right to parental leave Malaysia.
Prior to these amendments, the Employment Act in Malaysia only provided for paid maternity leave Malaysia. Male employees could be granted paternity leave at the discretion of their employers, as it was not legally mandated by the labor law Malaysia.
With the government’s introduction of parental leave Malaysia, organizations now prioritize leave management. This change provides better support for employees seeking a work-life balance while starting a family.
Is it compulsory for employers to provide parental leave Malaysia?

Yes, the Employment Act covers all employees, irrespective of their wages — which means that paternity and maternity leave Malaysia are statutory rights that employers owe to their employees.
Providing parental leave Malaysia helps an organization protect the well-being and mental health of their employees, fostering a safe environment that leads to higher employee engagement and reduced attrition rates. If an employer were to deny parental leave Malaysia to an eligible employee without proper justification, it would mean a violation of labor law Malaysia. This could result in legal issues, complaints, or disputes.
What is maternity leave Malaysia?
Maternity leave Malaysia is the authorized absence from work granted to a female employee in connection with childbirth by her employers. Maternity leave Malaysia is protected under the Employment Act.
Relevant reading: HR’s 2024 Guide to Singapore Maternity Leave
Section 2(1) of the Employment Act 1955 defines “confinement” as the period that begins at least 22 weeks into pregnancy and concludes with the birth of a child or children. If multiple children are born together, the confinement follows the birth of the last-born child.
Regarding maternity leave Malaysia:
- Employers cannot remove or decrease maternity benefits already specified in the employment agreement.
- It is expected that employers grant all female employees a minimum duration of paid maternity leave.
- Under the labor law Malaysia, employers are not permitted to terminate the contract of a female employee while she is on maternity leave Malaysia unless it is because of a business closure.
To be eligible, employees must fulfill these conditions as well:
- The employee must be employed for four months preceding confinement.
- The rights to maternity leave Malaysia only apply to the first five children of the female employee.
Maternity leave Malaysia also provides protection for female employees who are unable to return to work after the maternity leave period due to pregnancy-related health issues. Those who have this issue can retain their jobs for an additional 90 days beyond the standard leave period. Any termination within this extended time without appropriate medical certification of fitness for work is a violation of the labor law Malaysia.
Entitlement
Female employees are expected to inform employers of their maternity leave Malaysia, including the start date and expected confinement period, at least 60 days in advance.
If there’s any need to begin maternity leave earlier due to medical reasons, employees must make sure to communicate properly with the employer as soon as possible. Communication can help in promoting parental leave Malaysia as a budding work culture.
While on maternity leave, if a female employee gets certified fit to return to work by a registered medical practitioner, she is entitled to resume work at any time, with the consent of her employer under the labor law Malaysia.
The leave eligibility in the Employment Act 1955 is applicable to both Malaysian and foreign employees. Therefore, foreign female employees are entitled to maternity leave Malaysia and the allowance as well.
In the unfortunate event that a female employee suffers a miscarriage after at least 22 weeks of pregnancy, she is still entitled to maternity leave and allowance, as long as she meets the conditions outlined in the Act.
Duration
Maternity leave Malaysia was extended from the previous 60 days to 98 consecutive days for eligible female employees.
Commencement
Expectant mothers can take maternity leave Malaysia at any time, provided it begins no earlier than 30 days before their expected confinement date or extends beyond the day immediately following it. A doctor’s letter confirming the due date often endorses this flexibility.
Maternity allowance
Maternity allowance is the financial support given to female employees during their maternity leave. As stated previously, the minimum time for paid maternity leave Malaysia is 98 days.
According to the Act:
- An employee qualifies for maternity allowance if she has a total work history with the employer for at least 90 days within the nine months before her confinement.
- The maternity allowance is paid for the entire eligible leave period, which must span not less than 98 consecutive days.
- To qualify for the maternity allowance, the female employee must meet the employment duration criteria and not have five or more surviving children.
For instance, if a female employee who has been with a company for two years discovers she is pregnant, expecting to give birth in six months. She meets the eligibility criteria for maternity allowance, having fulfilled the required duration of employment.
However, the situation changes under the labor law Malaysia if she has only recently started working, for example, about two months before discovering her pregnancy with an expected delivery in six months. While she is entitled to maternity leave Malaysia, she would not qualify for the allowance. This is because she has not been employed for a minimum of 90 days within the nine months leading up to her confinement.
Termination of a pregnant employee
Under the provisions of maternity leave Malaysia, terminating the employment of a pregnant female employee or one experiencing pregnancy-related illnesses is considered unlawful.
There are specific circumstances like a willful breach of employment contract, misconduct, or business closure that could cause such termination. If the termination happens, according to the labor law Malaysia, the employer is expected to prove that the decision was unrelated to the pregnancy or any associated health issues.
What is paternity leave Malaysia?
Male employees get paid time off after becoming new fathers and this paid time is called paternity leave. Unlike maternity leave, paternity leave for new fathers remains relatively scarce worldwide.
Allowing male employees to take paternity leave not only allows them to be a part of their child’s beginning and also supports their partner during the postpartum period.
There’s an increasing recognition of the role of a father in a child’s upbringing, and businesses are beginning to acknowledge parental leave Malaysia. Paternity leave policies are different from those of employers; while some give the employee only the statutory minimum time, others can give up to 30 days of leave.
Entitlement
The entitlement for paternity leave is seven consecutive days.
Eligibility
According to the labor law Malaysia, to be eligible for the seven days of paid leave, male employees must meet the following conditions:
- Legal marriage: The employee must be legally married to the mother of the newborn. Paternity leave is only granted in the context of a recognized marital relationship.
- Length of employment: The new father must be employed with the same employer for a minimum period of 12 months immediately before the commencement of the paternity leave.
Notify employer
The employer mandates that a male employee inform them about his spouse’s pregnancy at least 30 days before the anticipated due date or as soon as the pregnancy is known.
This advance notice allows the employer ample time to make necessary arrangements for paternity leave, ensuring a smooth transition in the workplace. It’s important that both male and female employees do this for parental leave Malaysia.
Manage Parental Leave Malaysia Effectively with Omni
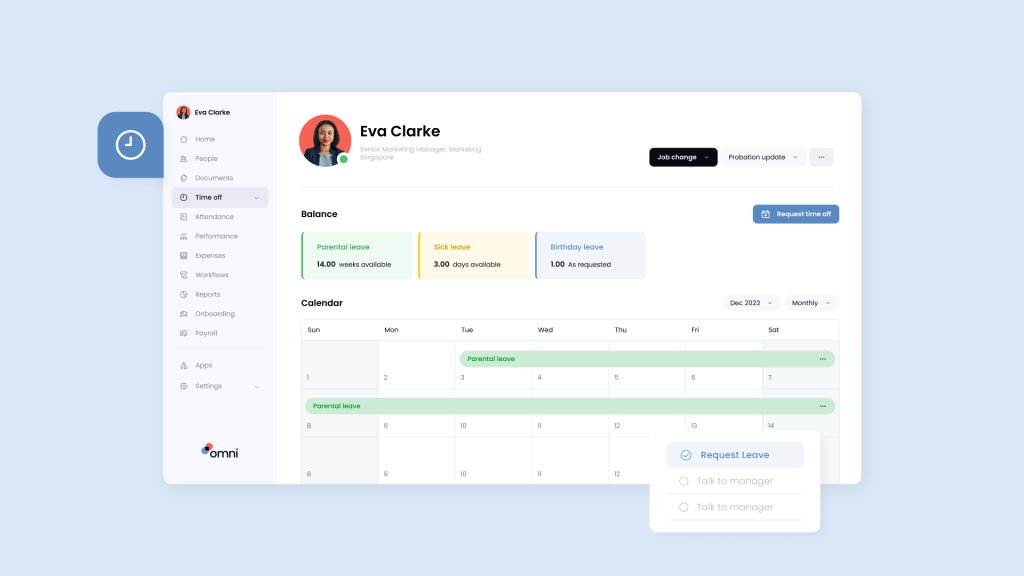
Parental leave Malaysia is a crucial benefit that supports employees in achieving a healthy work-life balance. With the recent amendments to labor law Malaysia have expanded parental leave Malaysia entitlements, emphasizing the importance of having the right HR tools to manage such benefits effectively.
Read next: The HR Tools Growing Teams Need in 2024
Omni’s all-in-one HRIS makes it possible to manage the entire end-to-end employee life cycle in one platform. Our robust time off management capabilities allow HR teams to streamline the management process of parental leave Malaysia. With customizable leave allowances, employers can set parental leave criteria based on Malaysian standards, company policies, or individual eligibility, simplifying compliance efforts and standardizing benefit allocation for their teams. These automated processes help HR professionals track eligibility, manage parental leave applications, and ensure proper reimbursement with ease, while ensuring employees get the time they need to recover and return to work productive and engaged.
Omni also seamlessly integrates with your team’s most loved work tools such as Slack, enabling managers to receive and manage time off approvals directly within the messaging platform, removing time-consuming steps from leave management with a quick push of a button. With automated calculations, employees and managers can easily view parental leave balances in real-time without the intervention of HR.
Our employee self-service portal empowers employees to swiftly submit their maternity leave requests, automatically routing to the appropriate managers with customizable approval workflows. And our user-friendly mobile application allows for on-the-go approvals and communication, so you can manage leave balances and employee benefits from anywhere.
Our localized solutions and unified system merges your parental leave Malaysia management efforts with payroll processing, facilitating automatic, accurate calculations and compliance with local regulations.
Book a demo with us today to learn more about how Omni can transform your parental leave management processes, saving you time, reducing administrative burdens, and enhancing overall efficiency.